Intel has been fighting hard-to-reduce latency between processing and storage.
In a recent announcement on the Intel Newsroom blog, Senior VP and GM of the NVM Solutions Group at Intel Corp. Rob Crooke spoke on the increasing importance of data-intensive tasks like business analytics to our society. At the same time, he noted how our methods of data processing and retrieval do not fully take advantage of recent CPU improvements.
“Historically, growth in memory performance has been much slower than increases in CPU performance, resulting in scenarios where the CPU is often waiting for data from storage.”
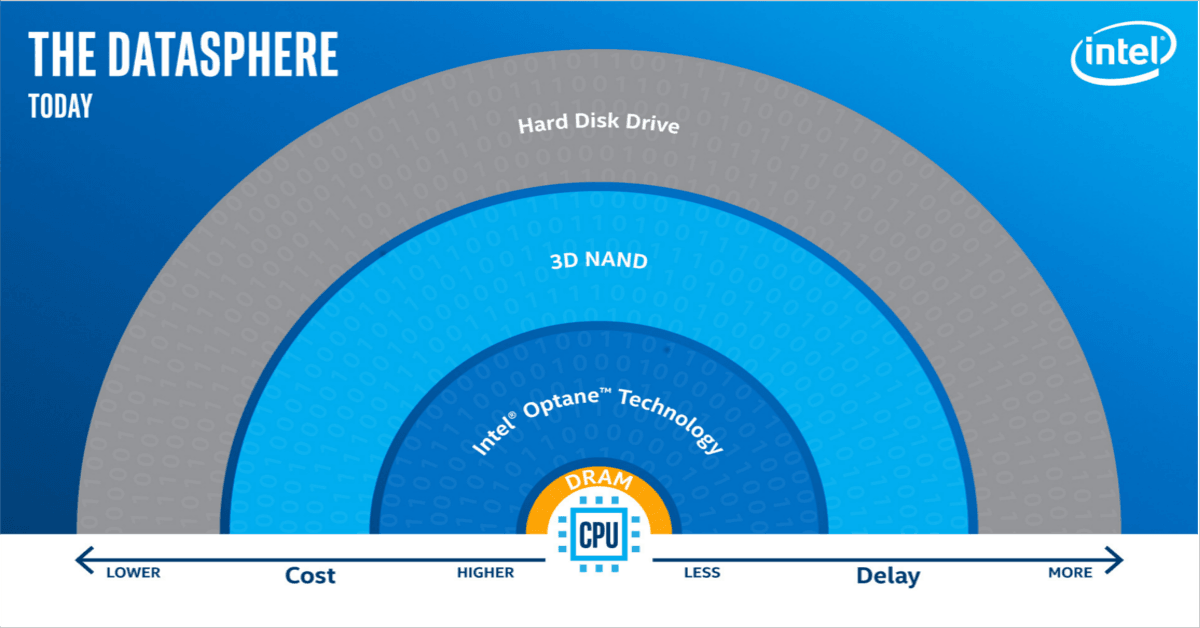
To the rescue comes Intel’s 3D Xpoint technology and developments in 3D NAND. New Intel SSDs and DIMMs will feature Intel® Optane™ which utilizes 3D XPoint Memory Media and dramatically reduce latency while bumping up the level of available storage closest to computing tasks. By removing data bottlenecks and thereby accelerating speed to knowledge, Intel and their partners hope to revolutionize the computing world beyond what Moore’s Law principles have already achieved.
More Computers Means More Data, Which Used to Mean More Latency
In the past few decades, CPUs and memory storage have become smaller than ever before. Coupled with wireless technology, these developments lead to an explosion of “smart” devices. Everything from cars to mobile phones to cameras contains a CPU these days. This influx of data invites new opportunities to process all of it and elicit enlightening discoveries that help us improve not just the way technology works, but society as a whole.
However, one major issue emerges as larger data sets queue up to be parsed. The ability for traditional hard drive technology and even NAND to read and write data has lagged behind swelling processor speeds.
How Intel Eliminates the Bottleneck
Basically the answer is to grow memory and storage at a faster rate. Intel has tapped into the potential by developing SSDs that can utilize high-density NVM storage technologies, including 3D NAND and their new non-volatile memory format developed in conjunction with Micron: 3D XPoint (pronounced “3D cross point”). Together, these technologies allow Intel to create ultra-fast, low-latency non-volatile storage solutions.According to Intel, these technologies sit comfortably between DRAM and NAND (the storage medium used in most SSDs today),, providing an optimal price to low-latency storage capacity ratio for cloud computing operations.
As Crooke states: “Bigger memory and faster storage provides significant value to the cloud, further enabling us to automate and efficiently analyze increasing quantities of data so businesses can run more efficiently. The need for storage and memory innovation is clear and the opportunity is big, whether it is for customer service, supply chain optimization, financial fraud detection, or precision healthcare research that is processing and analyzing larger genetic datasets in real time.”
You can learn more about how Intel is driving innovation with their developments in 3D XPoint by reading their post: “Computing and Data: Meant to Be Together”
You can also learn more about how Intel technologies and other developments like NVMe will forever change the way data storage tiering works by reading our latest informative blog posts.